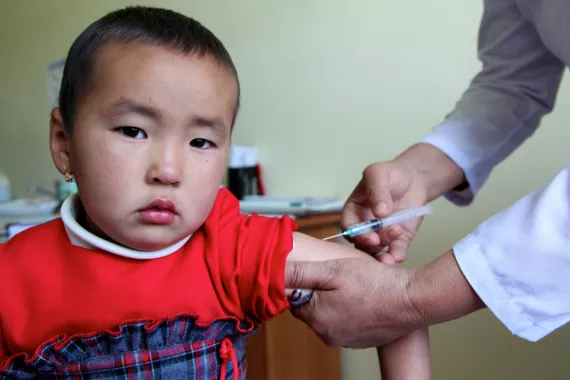
In 2023, more than 22,000 refusals of routine vaccination were registered in Kyrgyzstan, 48% of which are related to religious reasons, 24.kg reported. This marks a significant increase from the 12,000 refusals recorded in 2022.
Factors contributing to increase
The surge in refusals is attributed, in part, to the implementation of an integrated health information system. Gulbara Ishenapysova, the Director of the Republican Centre for Immunoprophylaxis highlighted that "Up to 48% of refusals are due to religious beliefs, more than 40% are due to doubts about the safety and effectiveness of vaccines, and another 10% refuse for other reasons".
Historical context
The RCI began tracking refusal statistics in 2016. “This is one of the important indicators for us,” Gulbara Ishenapysova noted. Efforts have been made to reduce vaccination refusals for religious reasons in collaboration with the Spiritual Administration of Muslims. As a result, the refusal rate has decreased from 78% in 2016-2017 to 48% in 2023. Despite this progress, the RCI continues to express concern over the issue.
Global statistics on vaccine hesitancy
Globally, 1 in 5 children still do not receive routine life-saving immunizations. In 2021, global immunization coverage for infants dropped to 81%, the lowest rate in over a decade. 25 mn children under the age of 1 year did not receive basic vaccines through routine immunization. This is 6 mn more than before the start of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2019.
Factors contributing to vaccine hesitancy
About half of the unvaccinated adults reported that they were concerned about possible side effects of the vaccine. About 42% reported that they “don’t trust the COVID-19 vaccine”. Less than 10% reported that they hadn’t gotten the vaccine because their doctor had not recommended it. About 2% reported not getting the vaccine because of difficulty obtaining it.
Follow Daryo's official Instagram and Twitter pages to keep current on world news.
Comments (0)