The European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD) has outlined its strategic priorities for Uzbekistan for the period 2024-2029. The focus is on supporting decarbonisation, green cities, water efficiency, cleaner energy, developing the private sector, fostering employment, skills, inclusion, digital transition, promoting economic governance, and business climate improvements, and enhancing infrastructure connectivity.

Uzbek economy: comprehensive overview
In 2022, the Uzbek economy demonstrated broad-based growth of 5.7%, buoyed by significantly improved conditions for both external and domestic demand. Exports of goods and services surged by 15.9% year on year, with notable increases in categories such as textiles, fruits, copper pipes, and electrical appliances, primarily to Russia. Domestic demand was further bolstered by a surge in money transfers and remittances, which saw an increase of 110% year on year in 2022, as well as the relocation of Russian companies and individuals.
The growth trend continued into January-September 2023, with real GDP rising by 5.8% year on year during this period. This growth was supported by increases in agriculture (+4.1% y/y), services (+12.1%), industry (+5.7%), and construction (+5.6%).

Inflation and monetary policy
Inflation reached double-digit levels in 2022 and stood at 9.0% as of August 2023. However, with inflationary pressures receding, the central bank decided to lower the policy rate by 100 basis points to 14% on March 16, 2023, in a bid to support economic activity.
As of September 2023, international reserves stood at $31bn, marking a decrease of 13.2% since the beginning of the year. Despite this decrease, the reserves remain sufficient to ensure adequate external buffers. As estimated by Fitch, the budget deficit was around 3.9% of GDP in 2022 and is expected to expand to 5.1% in 2023, before tightening to 4.1% in 2024.
Future outlook
Uzbekistan’s strong fundamentals, including robust external and fiscal buffers, low government debt, a young and industrious labour force, and a relatively diversified structure of the economy and external trade, bode well for the country’s ability to weather further global and regional shocks. The economy is projected to grow at 6.5% in both 2023 and 2024.
Comparison of new strategy with previous strategy (2018-2023)
Priority 1: enhancing competitiveness by strengthening private sector’s role in economy
Under the previous strategy, more than 230 SME advisory projects were carried out, including over 70 companies owned by women entrepreneurs and about 40 in rural areas. This led to improved access to finance for over 2,000 SMEs, providing €380mn credit lines through 9 partner banks and Uzbek leasing.
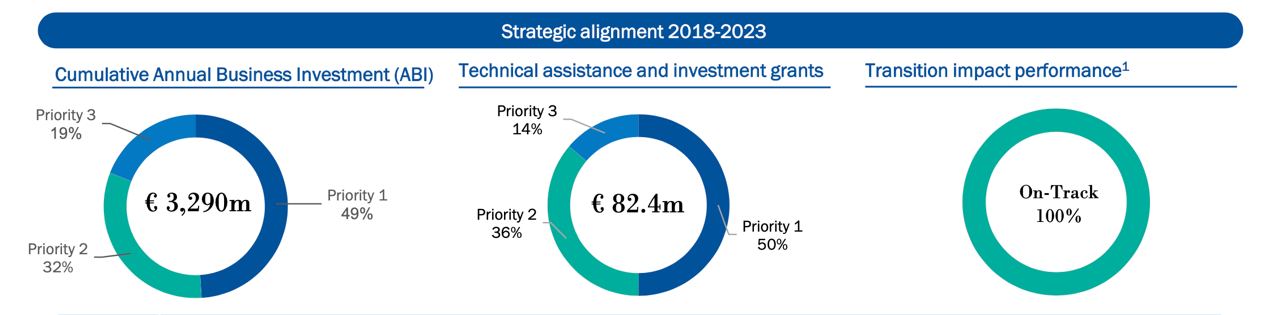
The EBRD spurred digital finance through an equity investment in Uzbekistan’s first fully digital bank, TBC Bank. It also helped develop financial and capital markets by leading the formulation of the Capital Markets Development Strategy, adopted in 2021, and investing in a $20mn cross-currency swap to facilitate currency risk management.
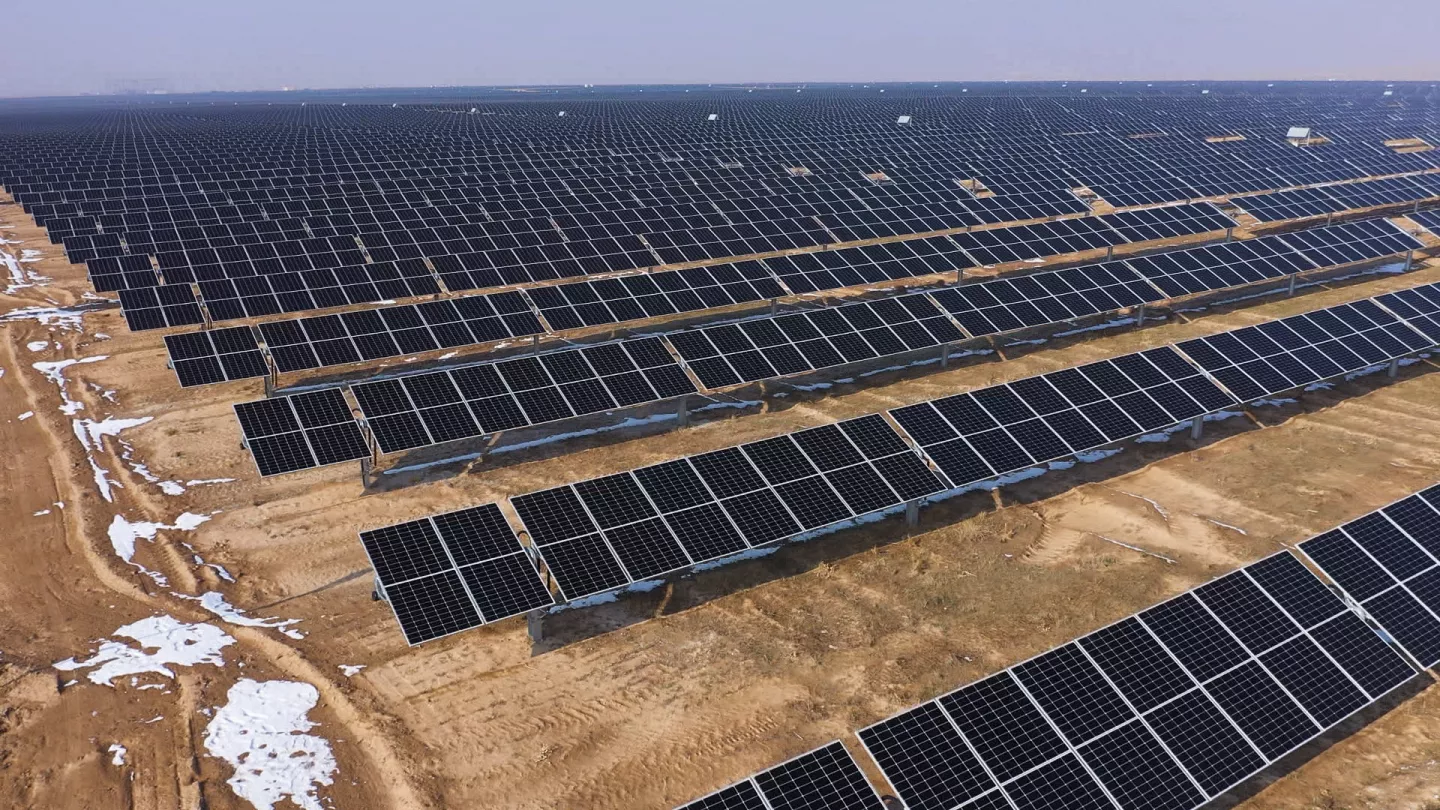
Priority 2: promoting green energy and resource solutions across sectors
The EBRD co-financed two privately owned solar photovoltaic plants in Uzbekistan, located in the Navoi and Samarkand regions, with a combined solar capacity of 200 MWh. This is equivalent to heating 20,000 homes for a year. Additionally, the EBRD invested $74mn in a 500MW wind power plant in the Navoi region, which introduced the 'Identiflight' system to monitor and detect species at risk of collision with wind turbines.
It also launched the Green Economy Financing Facility, supporting small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in investing in climate change mitigation and adaptation technologies. Furthermore, the EBRD played a key role in drafting a low-carbon pathway for Uzbekistan, aiming for carbon neutrality in the electricity sector by 2050. Moreover, the bank invested $50mn in Surkhandarya and $70mn in Namangan regions to support clean water supply and wastewater infrastructure development, benefiting 230,000 people with access to good quality water.

Priority 3: supporting increased regional and international cooperation and integration
To bolster regional and international cooperation and integration, over 1,100 transactions amounting to more than €690mn were completed through the Trade Facilitation Programme (TFP). This was complemented by face-to-face training for over 380 individuals from TFP partner banks, potential partner banks, and the Central Bank of Uzbekistan, along with 50 e-learning modules in 2023. A €71mn agreement was signed with Navoi Transmission to enhance energy connectivity by upgrading the regional electricity transmission network.
Tourism was boosted through investments in Khiva’s hospitality sector and the completion of the Khiva development masterplan under the Integrated Cultural Heritage Framework. Progress was made in improving transport infrastructure for better regional connectivity, including consultancy on the Tashkent - Samarqand toll road PPP. The PPP Law adopted in 2019 was supported, fortifying the legal and institutional frameworks for public-private partnerships. Lastly, a study funded by the EU on Sustainable Transport Connections between Europe and Central Asia was prepared, prioritising soft measures and investments.

Uzbekistan Country Strategy (2024-2029)
Priority 1: decarbonisation, green cities, water efficiency, cleaner energy
Key activities focus on supporting municipal infrastructure, water and wastewater investments, modernizing public utilities, improving irrigation systems, and undertaking uranium remediation projects. Additionally, the strategy includes initiatives such as Green Economy Financing Facilities for small and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs), promoting sustainability in the financial sector, providing policy advice on natural resources, facilitating the commercialization of mining companies, and emphasizing green governance.
The previous strategy (2018-2023) and the current Uzbekistan country strategy (2024-2029) demonstrate a clear alignment in Priority 2, which focuses on promoting green energy and resource solutions across sectors. The European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD) played a significant role in supporting renewable energy projects in Uzbekistan during the previous strategy. This included co-financing privately owned solar photovoltaic plants and investing in a greenfield wind power plant.

Priority 2: develop private sector and foster employment, skills, inclusion and digital transition
Both strategies align with their core objective of enhancing the role of the private sector in the economy. The 2018-2023 strategy focused on enhancing competitiveness by strengthening the private sector’s role in the economy. The new 2024-2029 strategy shifts the focus towards developing the private sector and fostering employment, skills, inclusion, and digital transition. It aims to expand financing for the private sector, foster foreign direct investment, and support the expansion of inclusive local supply chains. It also includes initiatives like Women in Business, Skills Councils, and the launch of the Youth in Business programme. The new strategy also emphasizes digitalisation in the private sector and the expansion of e-commerce.
Priority 3: promote economic governance and business climate improvements and enhance infrastructure connectivity
The strategies for 2018-2023 and 2024-2029 both emphasize the importance of regional and international cooperation and integration, but they approach this goal in different ways. The 2018-2023 strategy focused on facilitating trade, enhancing energy connectivity, boosting tourism, improving transport infrastructure, and supporting public-private partnerships. It also prioritized the development of sustainable transport connections between Europe and Central Asia.
On the other hand, the 2024-2029 strategy places a greater emphasis on improving economic governance and the business climate. This includes supporting the transformation of state-owned enterprises and banks, promoting public-private partnerships, and working on the SME Strategy for adoption in 2024. It also aims to improve the quality of institutions, strengthen the rule of law, and enhance regional and global connectivity. This strategy is more focused on policy advice, institutional reforms, and helping businesses and individuals improve access to finance and restructuring solutions.
Follow Daryo's official Instagram and Twitter pages to keep current on world news.
Comments (0)