Cooperation under the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) has played a pivotal role in driving global economic growth over the past decade, offering a ray of hope amidst mounting challenges in the world economy, such as a sluggish recovery and rising protectionism.
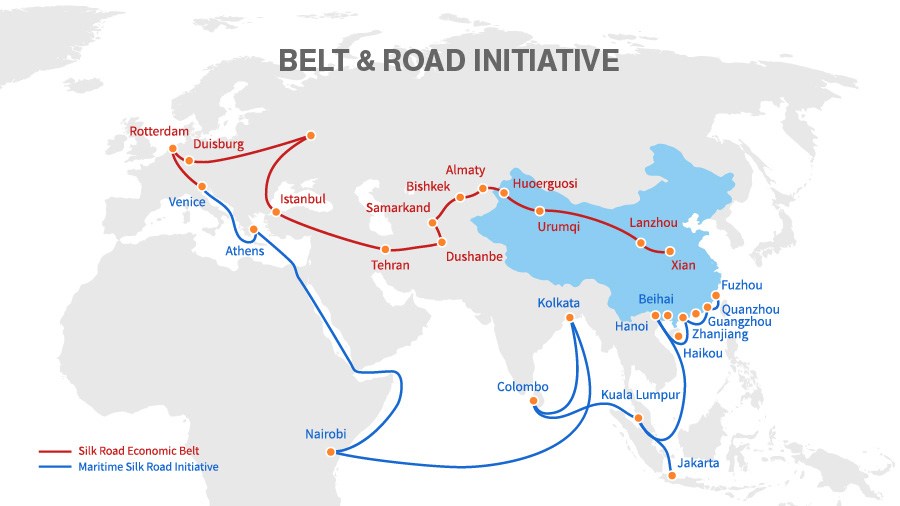
Expersts report that, remarkable achievements have been accomplished in various sectors, including trade and investment, global industrial and supply chains, and the promotion of balanced development since the BRI was first proposed in 2013.
He Weiwen, an expert with the China Association of International Trade, stressed the significance of infrastructure investment and the facilitation of trade and investment in boosting global economic growth. The BRI, he noted, has made substantial contributions in both these domains.
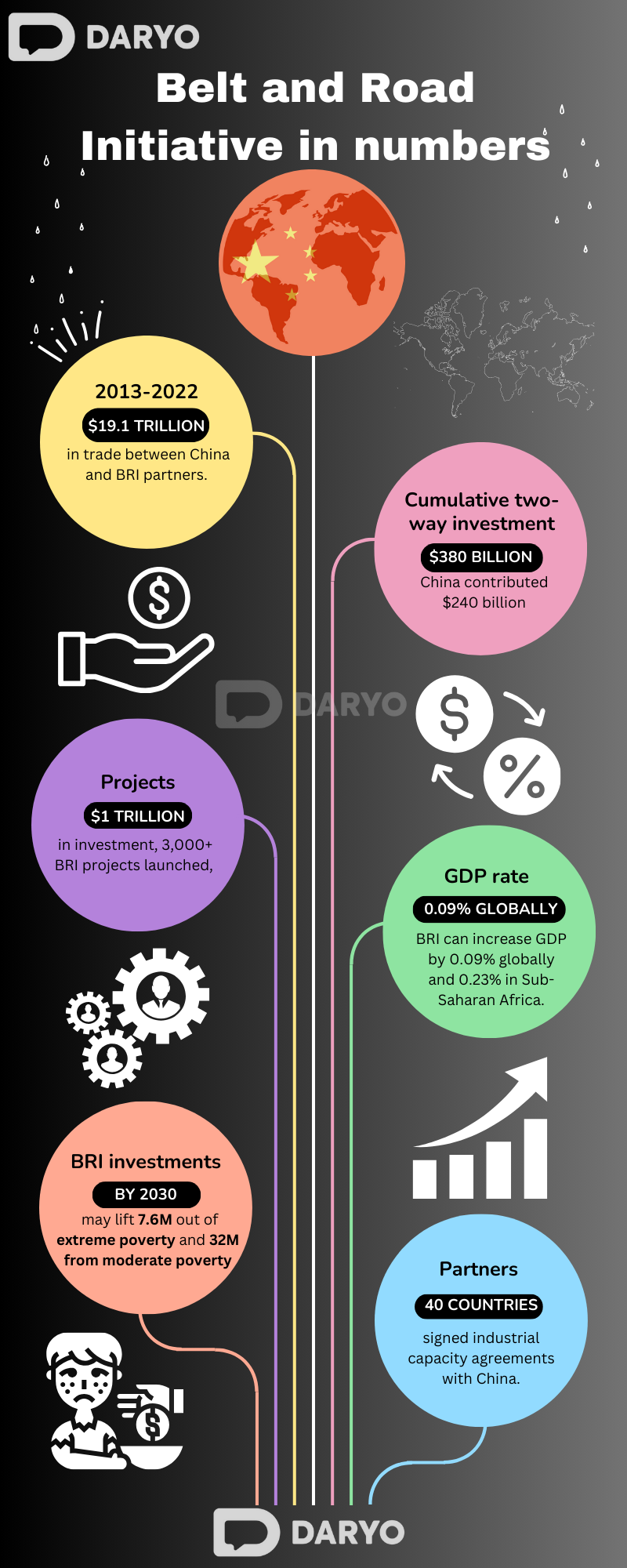
Key statistics from a white paper released by China's State Council Information Office reveal the extent of these contributions. From 2013 to 2022, the cumulative value of imports and exports between China and BRI partner countries amounted to a staggering $19.1 trillion, maintaining an average annual growth rate of 6.4%. Cumulative two-way investment between China and its partner countries reached $380bn during this period, with $240bn originating from China.
Over the past decade, more than 3,000 BRI cooperation projects have been initiated, involving nearly $1 trillion of investment. These projects have included the construction of vital infrastructure like railways, bridges, and pipelines, which have formed an extensive network connecting subregions in Asia and the continents of Asia, Europe, and Africa.
Liu Nanxing, an expert on international cooperation at the National Development and Reform Commission, emphasized that by improving infrastructure connectivity, BRI cooperation can significantly reduce international trade costs and enable underdeveloped countries, particularly those inland, to participate in global trade and pursue economic development.

Moreover, this interconnected infrastructure under the BRI framework has played a critical role in maintaining the stability and smooth operation of global industrial and supply chains, as pointed out by Hu Biliang, executive director of the Belt and Road School at Beijing Normal University. It has also provided much-needed energy and transport facilities for underdeveloped and developing countries, enabling them to join global industrial and supply chains.
Notably, by the end of June 2023, China had signed agreements on industrial capacity cooperation with more than 40 countries. More than 70 overseas industrial parks were established through collaboration between Chinese enterprises, partner countries' governments, and enterprises, as mentioned in the white paper.
"Projects for industrial capacity cooperation have helped BRI partner countries upgrade their industries for stronger competitiveness," Liu said.
Wang Lei, a scholar with the School of Government at Beijing Normal University, cited research results from the World Bank indicating that the proposed BRI transportation network and the consequent increase in foreign direct investment can raise BRI countries' GDP growth by 0.09% points. This includes a notable rise of 0.23% points in Sub-Saharan Africa.
Wang commented,
"This is truly remarkable. These are real tangible contributions made to global sustainable development."
One distinctive feature of the BRI is its inclusivity. By involving countries from different regions, at different stages of development, and with diverse cultures, the initiative has promoted open and inclusive growth at a time when globalization, driven predominantly by a few developed countries, led to imbalanced economic development.
Wang Fan, president of China Foreign Affairs University, underlined the global significance of the BRI as a platform for galvanizing the world economy. In a time marked by challenges including rising protectionism and international landscape volatility, the BRI does not seek to target any party, form cliques, decouple, or sever supply chains. Instead, it pursues common development for humanity with remarkable vitality and influence.
By June 2023, China had signed over 200 BRI cooperation agreements with more than 150 countries and 30 international organizations across five continents. The World Bank estimated that by 2030, BRI-related investments could lift 7.6mn people out of extreme poverty and 32mn out of moderate poverty.
Liu highlighted the BRI's role in advancing modernization for all countries, restructuring global value chains, and promoting mutually beneficial coexistence among all parties, invigorating a new model of international development.
Follow Daryo's official Instagram and Twitter pages to keep current on world news.
Comments (0)